Cardiac Nutrition is the cornerstone of a healthy heart. A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is paramount for preventing and managing cardiovascular disease. Imagine waking up each day with renewed energy and vitality, knowing that your heart is strong and resilient. Today’s article explores the crucial function of diet in heart health. Many people struggle with understanding how food choices affect their heart health and often feel overwhelmed by the information available. This article aims to offer clear, actionable strategies for crafting a heart-healthy diet. We’ll delve into crucial nutrients, offer practical tips, and discuss how to build a personalized nutrition plan for optimal heart health.
Understanding the Importance of Cardiac Nutrition
The Link Between Diet and Heart Health
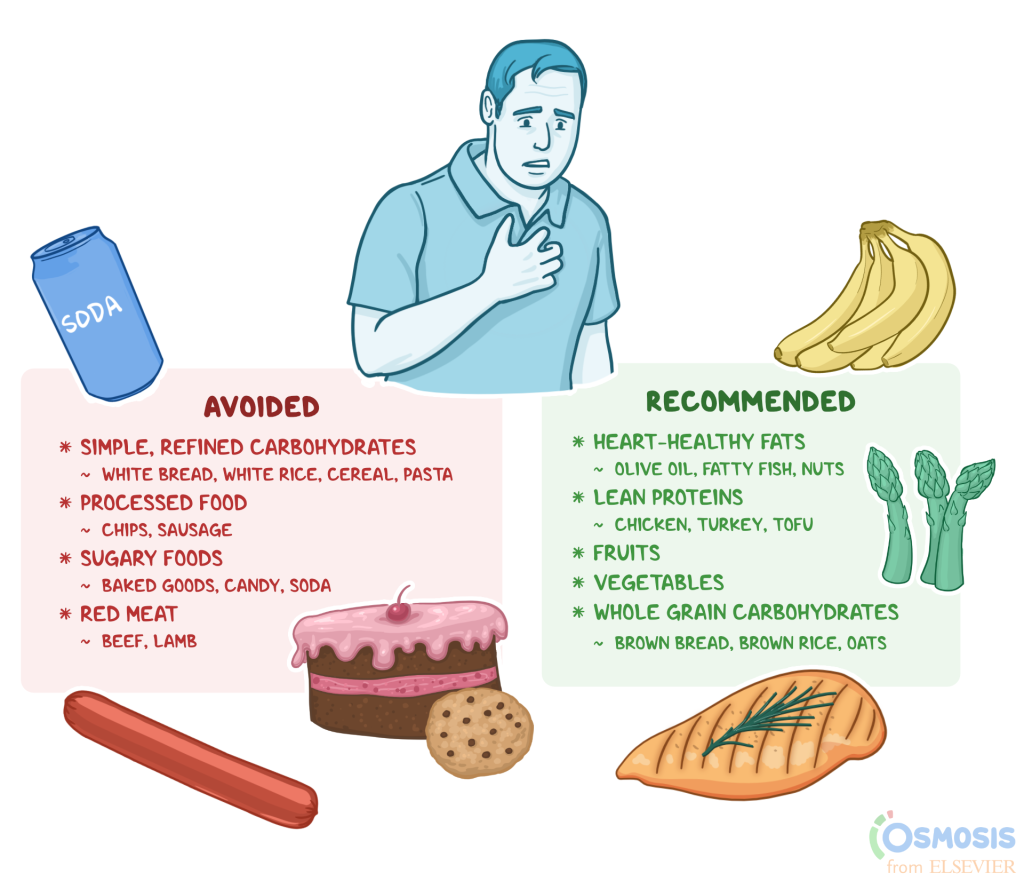
Maintaining a healthy heart is essential for overall well-being. Heart disease remains a leading cause of death globally, and a significant portion of this is attributed to lifestyle factors. A well-structured diet rich in essential nutrients plays a pivotal function in supporting cardiovascular health. This isn’t just about avoiding unhealthy foods; it’s about actively choosing foods that promote heart health, help maintain healthy cholesterol levels, and regulate blood pressure. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins into your diet can positively impact your heart’s health, offering significant protection against cardiovascular diseases.
Dietary Habits and Heart Disease Risk
Studies have shown that individuals with a diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, and sodium are at a substantially higher risk of developing heart disease. Dietary patterns can significantly impact blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels, all of which are directly linked to cardiovascular health. Making conscious choices about what you eat can dramatically reduce your risk of developing heart-related problems in the long run. It is crucial to focus on a diet that promotes healthy blood flow and minimizes the risk of blockages.
Essential Nutrients for a Healthy Heart
The function of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are a powerhouse of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. Vitamins C and E act as antioxidants that protect against cell damage and reduce the risk of blood clots. Fruits like berries, citrus fruits, and apples are loaded with fiber and essential nutrients. Vegetables such as leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts offer essential vitamins and minerals. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables is also associated with a lower risk of high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease.
The Importance of Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are essential for heart health, but it’s crucial to select the right ones. Oils like olive oil, avocados, and nuts are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and raise good cholesterol (HDL). These fats play a vital function in maintaining healthy blood pressure and reducing inflammation in the body. Including them in your diet in moderation is a great way to nurture your cardiovascular system.
Managing Cholesterol and Blood Pressure Through Diet
Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood. High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol are linked to an boostd risk of heart disease as they can accumulate in arteries, potentially leading to blockages. Conversely, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the body. A heart-healthy diet can help manage cholesterol levels by emphasizing foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins. By choosing the right fats and incorporating foods that promote HDL cholesterol, you can support healthy blood vessels and maintain proper circulation.
Controlling Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, puts a strain on your heart and blood vessels, increasing your risk of heart attack and stroke. Diet plays a significant function in controlling blood pressure. A diet high in sodium can raise blood pressure, so limiting processed foods, salty snacks, and excessive amounts of table salt is crucial. Foods rich in potassium, such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach, can help lower blood pressure. Controlling blood pressure is essential in maintaining a healthy heart.
Building a Personalized Cardiac Nutrition Plan
Understanding Your Individual Needs
Your individual needs and objectives regarding cardiac nutrition are crucial. Dietary recommendations should be tailored to your specific circumstances, including any pre-existing health conditions and medical history. Consult with a doctor or registered dietitian to develop a personalized plan. Factors such as age, activity level, and gender influence dietary requirements. A professional can accurately assess your needs and offer specific recommendations for a safe and healthy approach to cardiac nutrition.
Practical Tips for Implementing Changes
Gradually introducing changes to your diet is more effective and sustainable in the long run. Begin by making small, manageable swaps like replacing sugary drinks with water or choosing whole grains over refined grains. Slowly incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins into your daily meals will positively impact your heart health. Regular check-ups with your doctor will also be vital to assess the efficacy of your dietary changes.
Avoiding Common Dietary Pitfalls
The Dangers of Processed Foods
Processed foods are often high in sodium, unhealthy fats, and added sugars, which can contribute to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and weight gain—all of which negatively impact heart health. Limiting processed foods and opting for whole, unprocessed foods can significantly improve your cardiac health. By prioritizing whole foods, you’ll obtain the essential nutrients your body needs without unnecessary additives or unhealthy fats.
Overlooking Portion Control
Even healthy foods can be detrimental if consumed in excess. Portion control is key to maintaining a healthy weight and managing cholesterol levels. Being mindful of how much you’re eating is crucial for optimizing your cardiac nutrition plan.
Frequently Asked querys about Cardiac Nutrition
What are some quick and easy ways to incorporate more fruits and vegetables into my diet?
You can add a fruit salad to your breakfast or lunch or include a side of mixed vegetables with dinner. Snack on fruits like apples, bananas, or berries. Adding chopped vegetables to soups, salads, or stir-fries are also great options. Experiment with varied flavors and combinations to discover new favorites.
How can I reduce my intake of sodium without sacrificing taste?
select low-sodium seasonings and herbs to add flavor to your meals instead of salt. Rinse canned vegetables to reduce sodium text. Look for alternative flavorings such as lemon juice, vinegar, or spices like garlic, ginger, and chili flakes. Explore recipes that utilize fresh herbs and spices to heighten the flavor profile of your meals without relying on excessive amounts of sodium.
In conclusion, Cardiac Nutrition plays a vital function in maintaining heart health. By adopting a nutrient-rich diet, incorporating regular exercise, and managing stress levels, you can significantly reduce your risk of cardiovascular diseases. Prioritize whole foods, healthy fats, and lean protein sources, and consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations. Take charge of your heart health today and embark on a journey towards a healthier, happier you!