Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive condition affecting millions worldwide. It represents a significant global health concern, impacting individuals’ quality of life and potentially leading to kidney failure if left untreated. This article dives deep into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for chronic kidney disease to help readers understand this often-misunderstood condition. We will explore the critical function of early detection, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions in managing CKD, as well as preventing irreversible damage. This detailed guide will be structured with sections dedicated to symptom identification, various causes of CKD, and available treatment options, culminating in crucial preventive measures and actionable strategies for improved patient outcomes.
Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Symptoms and Early Detection
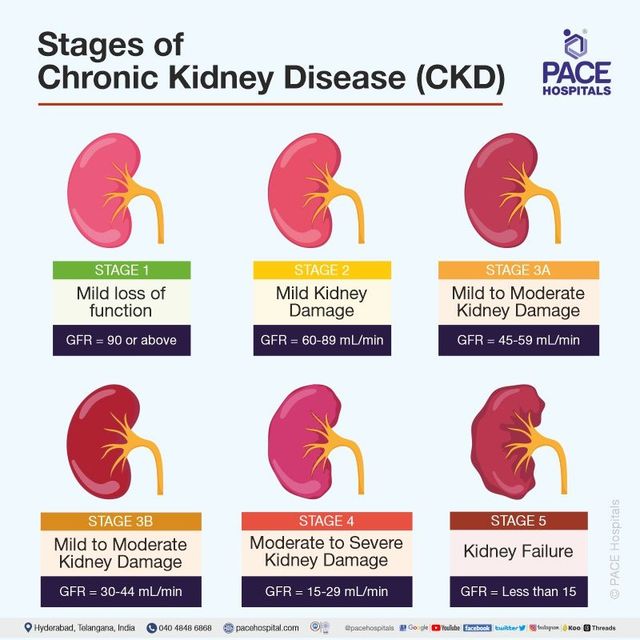
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a condition characterized by a gradual loss of kidney function over time. The kidneys’ function in filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood is compromised, potentially leading to severe complications if not addressed promptly. Early detection is crucial to manage the condition effectively and delay the progression to end-stage renal disease. Early symptoms are often subtle and may not be immediately recognized. Often, people with CKD may not experience any noticeable symptoms until the disease has progressed significantly. It’s crucial to note that certain demographic groups, such as those with pre-existing health conditions or a family history of kidney problems, may be at a higher risk of developing CKD.
Common Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
Feeling persistently tired, weak, or lacking energy can be an early indicator of CKD. The kidneys play a vital function in producing hormones and compounds vital for maintaining energy levels. Reduced kidney function can lead to a buildup of waste products in the bloodstream, hindering the body’s ability to produce energy.
Swelling in the Ankles, Feet, and Hands
Edema, or swelling in the ankles, feet, and hands, is another common symptom associated with CKD. This occurs due to the kidneys’ reduced ability to remove excess fluid from the body. The body’s fluid balance is disrupted when kidneys struggle to filter waste effectively, leading to fluid buildup in various parts of the body.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination, particularly at night (nocturia), may indicate kidney problems. The kidneys are responsible for regulating the balance of water and electrolytes in the body. When kidneys function less effectively, this balance is disrupted, causing disturbances in urinary output.
Changes in Urine Output
Changes in urine output, including diminished quantity or persistent cloudy or foamy urine, can be a warning sign of CKD. The kidneys are vital in filtering waste from the blood, and reduced kidney function can lead to changes in the composition and volume of urine.
Persistent Itching
Persistent itching, or pruritus, is an often-overlooked symptom of CKD. It arises from the accumulation of waste products in the blood, affecting the skin and nerves. These waste products can cause a sensation of itching, which can be quite uncomfortable and significantly affect quality of life.
Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease
High Blood Pressure
Hypertension is a significant risk factor for developing CKD. High blood pressure puts excessive strain on the delicate blood vessels of the kidneys. Sustained high blood pressure damages the filtering units (glomeruli) and nephrons, progressively reducing the kidney’s ability to function properly.
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, both type 1 and type 2, are leading causes of CKD. Elevated blood sugar levels damage the delicate blood vessels and nerves of the kidneys, interfering with the proper function of the nephrons, the kidney’s filtering units. Long-term exposure to high blood sugar can lead to irreversible kidney damage.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis encompasses a group of disorders affecting the filtering units of the kidneys (glomeruli). Inflammation of these vital components can outcome in a loss of function, potentially leading to CKD. Factors such as infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications can contribute to the development of glomerulonephritis.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Inherited genetic disorders, such as polycystic kidney disease (PKD), can cause cysts to form on the kidneys. The cysts eventually accumulate, leading to reduced kidney function and increasing risk of kidney failure.
Urinary Tract Obstructions
Obstructions within the urinary tract, whether due to tumors, stones, or other factors, can lead to boostd pressure in the kidneys. This chronic pressure can cause damage to the kidney tissues and contribute to the development of CKD.
Treatment Options for Chronic Kidney Disease
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle choices can play a significant function in managing CKD. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques are beneficial. Dietary adjustments, including limiting sodium and protein intake, can help alleviate the strain on the kidneys and promote better overall health. Regular exercise can lower blood pressure and improve blood sugar levels, both crucial in slowing the progression of CKD.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions contributing to CKD. Blood pressure medications, diabetes medications, and pain relievers may be utilized. The specific medications and dosages will vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and medical history. The aim is to control the progression of CKD and its associated complications.
Dialysis
Dialysis is a life-saving treatment option for individuals with advanced CKD when kidney function is severely impaired. There are two main types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis involves filtering the blood using an external machine, while peritoneal dialysis involves filtering the blood using the lining of the abdomen. The choice between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis will depend on various factors, including the individual’s lifestyle and preferences.
Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplantation is a surgical procedure in which a healthy kidney is transplanted from a donor into a recipient with CKD. This procedure can restore kidney function and significantly improve the recipient’s quality of life. Kidney transplantation is often a viable option for individuals with end-stage renal disease, and requires careful matching of the donor and recipient.
Prevention Strategies for Chronic Kidney Disease
Maintaining Healthy Blood Pressure
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels is paramount in preventing CKD. Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure, including lifestyle modifications and medications, can greatly reduce the risk of kidney damage.
Managing Diabetes Effectively
Effective diabetes management is crucial in preventing CKD. Maintaining optimal blood sugar control through diet, exercise, and medication is essential.
Regular Kidney function Testing
Regular kidney function tests are essential for individuals at high risk of developing CKD. Early detection enables timely intervention and management.
Adopting a Healthy Diet and Lifestyle
Adopting a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fat, coupled with regular exercise, can promote overall well-being and kidney health.
Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption is critical for kidney health. These habits significantly boost the risk of kidney damage.
Frequently Asked querys
What are the early signs of chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
Early signs of chronic kidney disease (CKD) can be subtle and often overlooked, making early detection challenging. Early indicators may include persistent fatigue and weakness, swelling in the ankles, feet, and hands, frequent urination, especially at night, changes in urine output (reduced quantity or persistent cloudy/foamy urine), and persistent itching (pruritus). The absence of noticeable symptoms does not necessarily mean the individual is complimentary from CKD; regular checkups and kidney function tests are essential, especially for high-risk groups. It’s vital to remember that early detection allows for timely intervention and management to slow disease progression.
What are the risk factors for chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
Several factors boost an individual’s risk of developing chronic kidney disease (CKD). High blood pressure is a major risk factor, as it strains the delicate blood vessels within the kidneys. Diabetes mellitus, both type 1 and type 2, significantly contribute to CKD development due to the damage high blood sugar levels cause to the kidney’s filtering units. Furthermore, certain genetic conditions, like polycystic kidney disease (PKD), and urinary tract obstructions can lead to kidney damage and boost the risk of CKD. Individuals with a family history of CKD or pre-existing health conditions should be particularly vigilant about their kidney health and seek regular medical checkups.
In conclusion, Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a serious health concern that requires early diagnosis and proactive management. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available therapy options is crucial for effective patient care. By recognizing the early warning signs and seeking professional medical advice, individuals can significantly improve their chances of managing CKD and maintaining a high quality of life. Consult your doctor for personalized guidance and treatment plans. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can play a vital function in mitigating risk factors and preventing further kidney damage. Learn more about CKD prevention by visiting our website today!