Premature baby care is a complex and multifaceted area requiring a thorough approach that combines medical expertise with emotional support. This article delves into the multifaceted challenges and crucial support systems available for parents and caregivers of premature infants, highlighting strategies for fostering healthy development and navigating the unique needs of these vulnerable newborns. Addressing the specific needs of premature babies requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing medical interventions, parental support, and long-term developmental care. This article will examine the key challenges of premature infant care and explore the diverse support systems available to ensure a positive trajectory for these vulnerable infants. It will cover critical facets such as medical interventions, developmental milestones, the importance of parental support, and the long-term implications of prematurity. The structure will delve into the challenges faced by parents, highlighting available resources and strategies.
Understanding the Challenges of Premature Birth
Defining Premature Birth
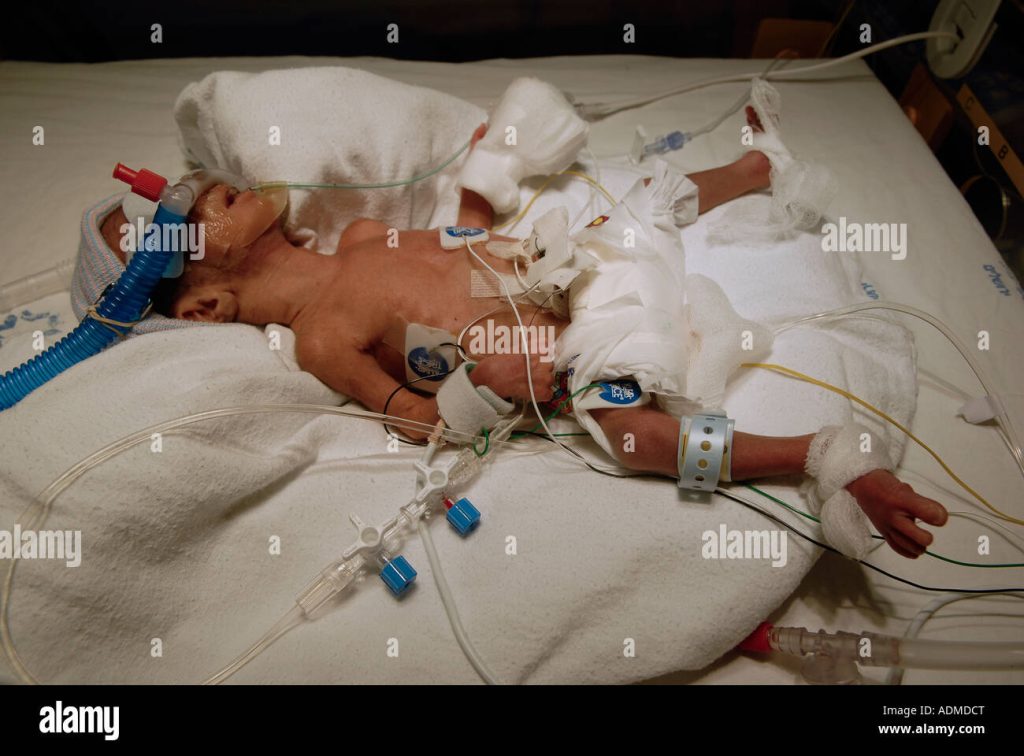
Premature birth, also known as preterm birth, occurs when a baby is born before 37 weeks of gestation. This can have profound effects on the baby’s health and development, potentially leading to a scope of complications, which necessitates specialized care and support. These infants often face significant medical challenges as their bodies are still developing and may not be fully prepared for life outside the womb. The impact of premature birth encompasses a broad spectrum of physical and developmental issues. Prematurity often outcomes in a weakened immune system, making the infant susceptible to infections. Breathing difficulties are also common, requiring the need for ventilators and specialized respiratory support. Nutritional challenges are also prominent, requiring the implementation of nutritional strategies to ensure proper growth and development. These difficulties place a tremendous strain on both the child and the family.
Medical Interventions for Premature Infants
Intensive Care and Monitoring
Providing optimal care for premature infants often involves a multidisciplinary approach. Critical medical interventions, such as mechanical ventilation, nutritional support, and medication administration, are frequently required to stabilize and sustain the baby’s health. Monitoring vital signs, such as heart rate, respiration, and body temperature, is crucial to ensure ongoing safety and to detect any potential complications. For instance, studies have shown that early detection of respiratory distress syndrome, a condition that commonly affects premature infants, can significantly improve their chances of survival and long-term health.
Developmental Milestones and Support
Early Intervention Programs
The developmental needs of premature infants often require specific attention and intervention. Early intervention programs play a crucial function in stimulating growth and development. These programs often incorporate therapies and activities designed to promote physical, cognitive, and social development. For example, physiotherapy and occupational therapy can help premature infants develop motor skills, while speech therapy addresses communication challenges. Early intervention is key in addressing potential developmental delays and fostering healthy growth and development. For example, studies consistently show that infants who participate in early intervention programs often achieve better developmental outcomes compared to their peers who do not receive these services.
Parental Support and Resources
Navigating the Emotional Toll
The journey of caring for a premature infant can be emotionally challenging for parents. Financial burdens and the need for extended hospital stays can place significant strain on families. Providing adequate support systems for parents is critical. For instance, emotional support groups offer a safe space for parents to share their experiences, offering encouragement, and reducing feelings of isolation. Access to information, education, and emotional support can positively impact the family. Support groups offer a framework for parents to share their experiences and gain encouragement. The physical demands of caring for a premature infant are considerable; providing resources that facilitate better sleep for parents are crucial for emotional well-being.
Long-Term Implications and Outcomes
Monitoring Growth and Development
The long-term implications of prematurity often extend beyond the initial hospital stay. Longitudinal studies reveal the importance of ongoing monitoring and interventions to support healthy development and address potential long-term issues. For instance, studies show that premature infants have an elevated risk of developing long-term medical problems, such as asthma, cerebral palsy, and learning disabilities. Early identification and management of potential long-term issues are essential.
Example of achievement Stories
Case Study of a Premature Infant
Sarah, a new mother, and her husband were faced with a multitude of challenges caring for their premature baby. They received counseling and support from the hospital, which included a resource program on newborn care. The program focused on creating a supportive environment for families with premature infants. The program emphasized parental education and support. In addition, Sarah and her husband received financial assistance and information about additional resources.
Importance of Early Intervention
Future Directions and study
Conclusion of the Article
Frequently Asked querys
What are the common challenges faced by parents of premature infants?
Parents of premature infants face numerous challenges, from the emotional stress of the situation to the financial burden of extended hospital stays and specialized care. The anxiety surrounding the baby’s health and the constant worry about their future development can take a toll on parents’ mental and emotional well-being. Practical support, such as financial assistance, educational programs about newborn care, and access to counseling services, can help alleviate these pressures and enhance the family’s overall resilience.
How can families access support systems for premature babies?
Families can access a scope of support systems for premature babies, including support groups, community-based programs, and online resources. Support groups offer a vital network for sharing experiences, advice, and encouragement among parents of premature infants. Community programs offer practical assistance, such as financial aid and childcare resources, while online resources offer access to informative articles, videos, and forums where parents can connect with others. These collective resources can significantly mitigate the challenges faced by families navigating this demanding journey.
In conclusion, premature baby care presents unique challenges demanding thorough support systems. Understanding the specific needs of these vulnerable infants, along with access to specialized medical care and parental support, is crucial for their achievementful development and well-being. Further study and initiatives are needed to address the disparities and improve outcomes for premature babies worldwide. For parents facing these challenges, consider reaching out to support groups, consult with healthcare professionals, and explore resources designed to assist families navigating this journey. This proactive approach can significantly impact the development of these precious little ones.