Hair Loss Due to Autoimmune Diseases is a significant concern impacting many individuals. Imagine waking up one morning and noticing noticeable thinning or hair shedding, a condition that can be deeply distressing and impact self-esteem. Autoimmune diseases are a leading cause of hair loss, and understanding the connection is vital for appropriate medical intervention. This thorough guide will explore the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatments, and management of hair loss linked to various autoimmune diseases. It will also shed light on support systems to aid individuals throughout their journey.
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases and Hair Loss
What are Autoimmune Diseases?
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and cells. This attack can disrupt various bodily functions, including hair follicle health, often outcomeing in significant hair loss. Numerous factors contribute to autoimmune-related hair loss, including genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and hormonal imbalances. Understanding these intricate mechanisms is essential for personalized treatment plans. Approximately 5-8% of the population is estimated to experience hair loss related to autoimmune diseases. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized care.
determineing the Symptoms of Hair Loss
Recognizing Hair Loss Patterns:
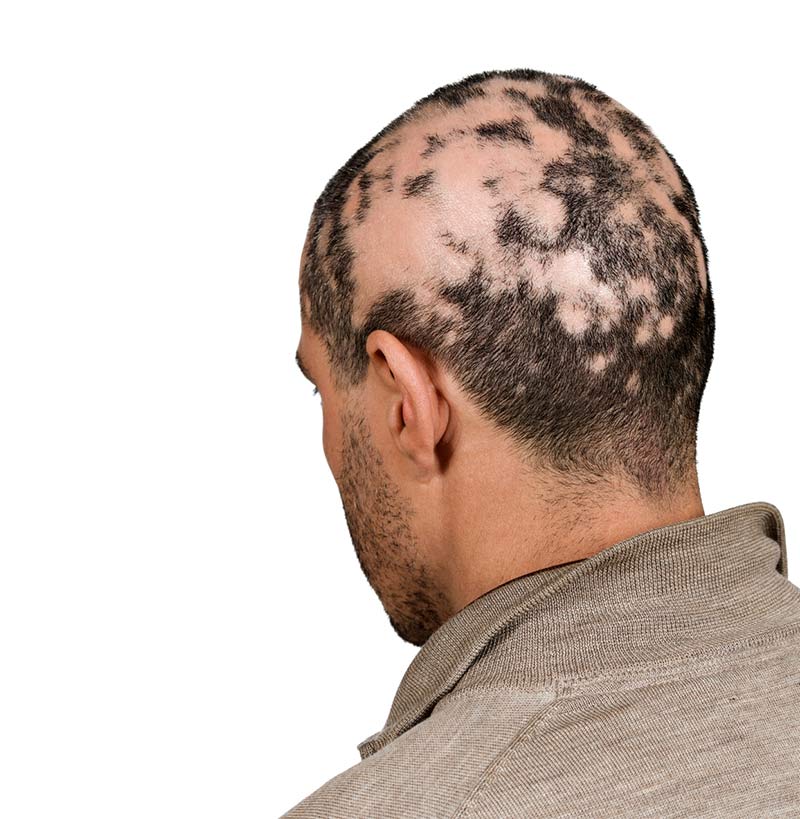
Recognizing the symptoms of hair loss due to autoimmune diseases is essential for timely intervention. While the experience varies greatly based on the specific disease and individual, common symptoms include diffuse thinning (all over), patchy hair loss, and significant shedding. For example, in alopecia areata, individuals may experience sudden patches of hair loss on the scalp, face, or eyebrows. Additionally, the degree of hair loss can scope from mild to severe, highlighting the need for individualized assessment. Studies have shown that prompt medical attention and early intervention can significantly improve the patient’s outlook and recovery. Detailed examination of the hair loss pattern is essential to determine the underlying cause.
Common Autoimmune Diseases and Hair Loss
Alopecia Areata
A common autoimmune condition that causes sudden, patchy hair loss. In alopecia areata, the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. This condition can affect anyone at any age, often causing significant psychological distress. Treatment often involves topical medications or immune-modulating therapies tailored to the specific needs of the patient. A recent study showed a correlation between stress levels and boostd instances of hair loss.
Lupus
Lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, can manifest in various ways, including hair loss. The specific mechanism of hair loss in lupus is complex, possibly linked to inflammation and immune system dysfunction. Patients with lupus often experience a scope of symptoms, some of which may be overlooked by patients. Early diagnosis and targeted treatment are crucial to controlling lupus symptoms and minimizing hair loss. In addition, regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the disease’s progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Thyroid Conditions
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can profoundly impact hair health. Imbalances in thyroid hormones can interfere with hair follicle growth and lead to noticeable thinning or shedding. Thyroid conditions often affect other bodily functions beyond hair health, making early detection crucial. Early diagnosis and management of thyroid problems are critical to preventing further hair loss and restoring normal function. It’s crucial to note that hair loss is often just one symptom, and a full evaluation is essential.
Frequently Asked querys
What are the steps to take if I suspect hair loss is related to an autoimmune disease?
Visit a dermatologist or rheumatologist. They will conduct a thorough evaluation, considering your medical history and symptoms. This may include physical examinations, blood tests, and potentially a skin biopsy to determine potential underlying causes. Early intervention is key to effective management and treatment. Taking proactive steps to address potential autoimmune-related hair loss can significantly improve the prognosis.
How can I manage hair loss related to autoimmune diseases?
Managing hair loss linked to autoimmune diseases often involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments. Treatment plans will vary greatly depending on the specific disease and its progression. Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare offerr are essential for monitoring your condition and adjusting the treatment plan as needed. Furthermore, a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, stress management techniques, and a consistent sleep schedule can aid in managing the condition effectively.
In conclusion, Hair Loss Due to Autoimmune Diseases is a complex issue requiring a multifaceted approach. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention, and exploring available treatment options are crucial steps towards managing the condition effectively. This article offerd a thorough overview of the various autoimmune diseases linked to hair loss, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate management strategies. Consult a dermatologist or rheumatologist for personalized advice and treatment plans specific to your condition. You can also explore support groups and resources for emotional support and guidance throughout your journey. Remember, managing hair loss associated with autoimmune diseases requires a combined effort of medical professionals, patients, and support systems. Take control of your health and well-being by proactively seeking help and information.